[unity] static bool 이랑 static으로 지정해주지 않는 bool의 차이점
내가 쓸데없는 고민을 하고 있는 줄 알았는데, 역시 인간들은 다 비슷하게 생각한다는 걸 항상 느낀다 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ
Don’t understand static boolean behavior
예.. 저도 그렇게 생각합니다…- 링크는 stackoverflow에 올라온 질문이다. 본문을 보고 싶으면 제목 클릭 ㄱㄱ
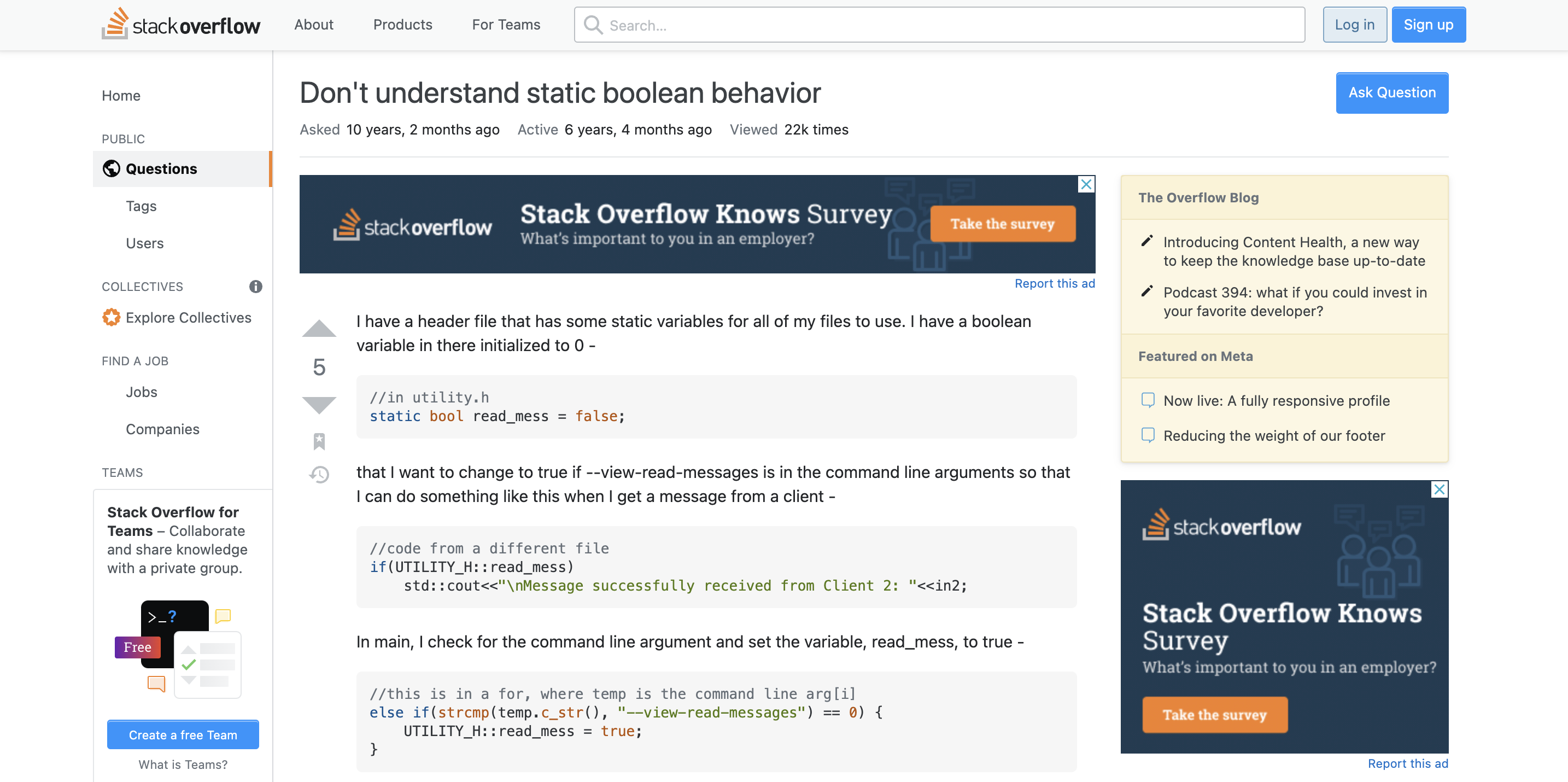

static: “local”의 의미를 가진다. ( ↔ ‘전역’변수 : global variable) : static in this context means “local” (to the translation unit).- 로컬 변수라고 하면, 각 로컬마다 다른 값을 가질 수 있다는 거 아닌가..? 내가 static을 잘못 이해하고 있었나?
- There will be multiple copies of
read_messin your program, one per translation unit which is not the same thing as a header file. - In your case you can most likely approximate “translation unit” as
.cppor.cor.ccfile뭔소리야… -
what you meant to do was to declare an extern variable, or static class member and define it in just one translation unit.
ㅇㅇ 나도 그거 하고 싶은데 
- static global variables are privates to each .c or .cpp file (or translation unit). If you print out the address of read_mess (e.g., printf(“%x”, &read_mess);), you will see different addresses, which means two separate copies of the boolean variable exist.
- local ↔ global
- static ↔ ???
- ** SOLUTION : remove
statickeyword, or replace withextern** - C#에서도 extern 키워드가 있나?
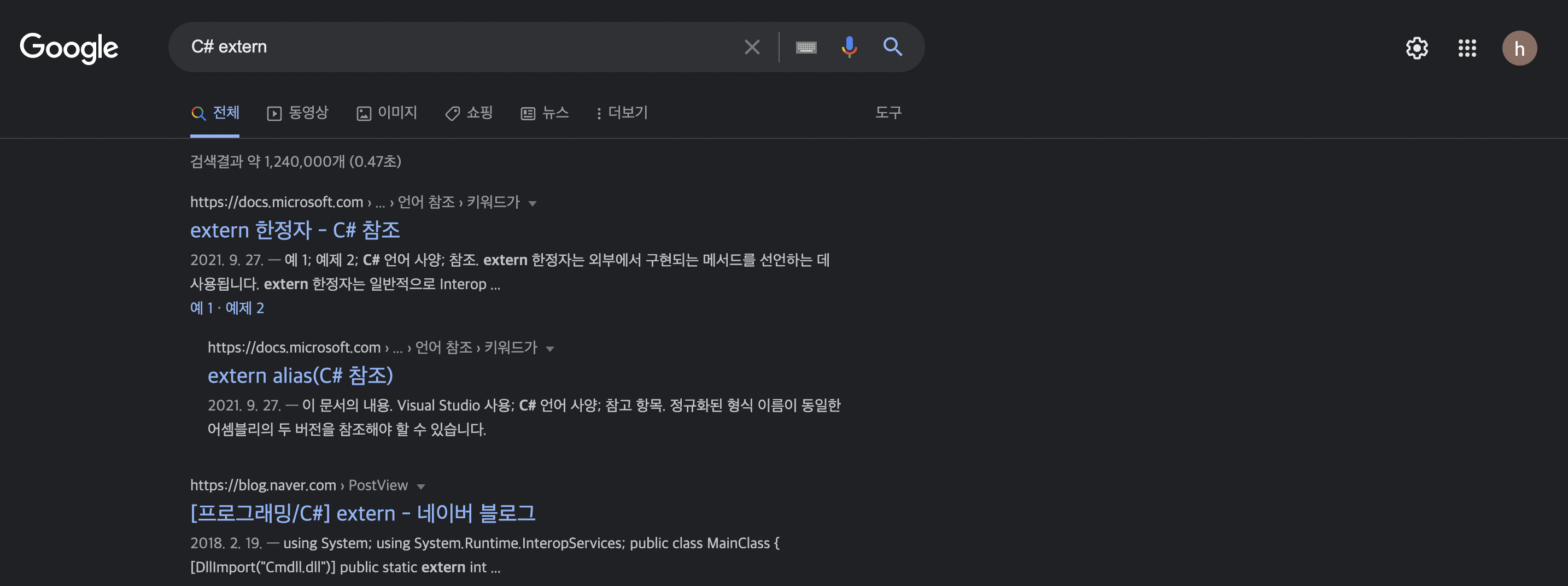
ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅁㅊ있네…. 당장 script 수정간다…
Header File이란?
컴퓨터 프로그래밍에서, 특히 C와 C++ 프로그래밍 언어에서, 헤더 파일(header file) 또는 인클루드 파일(include file)은 컴파일러에 의해 다른 소스 파일에 자동으로 포함된 소스 코드의 파일이다. 일반적으로 헤더 파일들은 다른 소스 파일 속의 첫 부분에 포함된다.
Translation Unit이란?
- In C and C++ programming language terminology
- A translation unit (or more casually a compilation unit) is the ultimate input to a C or C++ compiler from which an object file is generated.
- A translation unit roughly consists of a source file after it has been processed by the C preprocessor
- Header files listed in #include directives are literally included, sections of code within #ifndef may be included, and macros have been expanded.